Interaction to Next Paint: Make Way for the New Core Web Vital
/This blog post highlights the change in core web vitals coming from Google in early 2024. Seven Elm can help diagnose any Core Web Vitals issues on your site. If interested in learning more, please contact us.
Introduction
Google recently made an important announcement regarding Core Web Vitals, introducing the “Interaction to Next Paint” (INP) as a pending vital. Set to become official in March 2024, this new metric will replace the current “First Input Delay,” (FID) which has been in place since May 2020.
The Interaction to Next Paint metric measures how quickly a web page provides visual Feedback to users after interacting with any element of the page post-loading, offering a more comprehensive view of a website’s responsiveness throughout the user’s experience.
While it represents an improvement in measuring web performance, it also presents a new challenge for website owners in ensuring their sites meet the new standard to reap benefits such as better SEO rankings.
Core Web Vitals and Their Importance
Introduced by Google in May 2020, Core Web Vitals simplify and standardize the metrics by which site owners can gauge their website’s performance and users’ quality of experience.
Google’s WebDev Blog states,
“Site owners should not have to be performance experts to understand the quality of experience they deliver to their users. The Web Vitals initiative aims to simplify the landscape and help sites focus on the metrics that matter most, the Core Web Vitals.”
Ensuring that your website’s Core Web Vitals are performing well holds several significant advantages, including:
SEO Ranking Boost: Core Web Vitals are crucial in SEO rankings. By optimizing for these metrics, you can improve your site’s visibility in search results.
Mobile Search Dominance: With mobile-first indexing, good web vitals enhance visibility for mobile users, representing a significant portion of online traffic.
Reduced Bounce Rates: Faster loading times and responsiveness lead to lower bounce rates. Positive user experiences signal relevance to search engines.
Featured Snippets and Rich Results: Websites with good Core Web Vitals have a higher chance of appearing in featured snippets and rich results, boosting visibility and attracting organic traffic.
While these benefits are essential for site owners, users benefit from sites with excellent Core Web Vitals, especially regarding overall user experience. Sites that fail to meet user expectations in terms of performance may lead to higher bounce and lower conversion rates.
Contact Seven Elm today for a free evaluation of your web performance using industry standard tools.
Understanding Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
As mentioned earlier, the Interaction to Next Paint metric presents a broader view of a user’s interaction with a website. Unlike First Input Delay (FID), which only measures the time until a user’s first interaction with a page, INP focuses on how fast dynamic elements of a page react to user interactions. One way to think about it is that FID measures a user’s first impression of a page, INP measures the user’s complete experience on the page.
In technical terms, Interaction to Next Paint measures how quickly a webpage provides Feedback to the user after an interaction.
The Importance of Interactions
Google offers a list of interactions that INP measures, emphasizing the importance of timely responses to keep users engaged. These include mouse clicks, screen touches, and keyboard presses.
Google will measure the time between the event and the behavior for this Core Web Vital. The longer it takes, the less Feedback the user receives, resulting in a poorer user experience. To illustrate this, let’s consider an e-commerce site where you click to expand product details, and nothing happens for several seconds until the content loads. This frustrating experience can lead users to (rage) click repeatedly, triggering unintended actions and causing them to abandon the site.
Feedback keeps users engaged and informed as the application processes their requests. For instance, the site should show a loading message or icon immediately after the user clicks. This Feedback shows their request is processing.
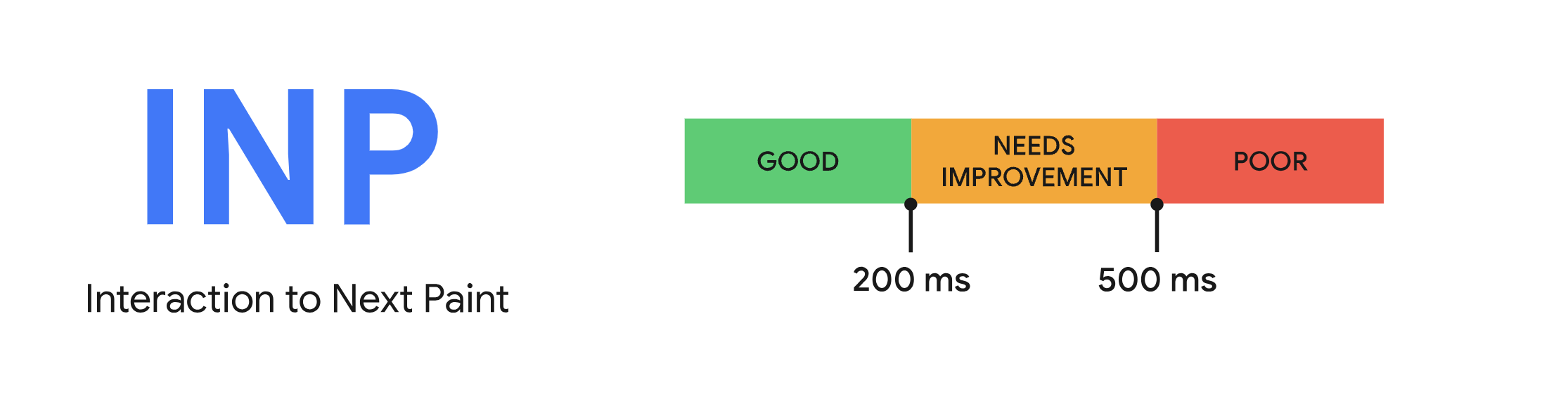
What Makes for a Good INP?
Google lays out what makes for a good, mediocre, and poor INP on their Web.dev INP article.
An INP below or at 200 milliseconds means your page has good responsiveness. An INP above 200 milliseconds and below or at 500 milliseconds means your page’s responsiveness needs improvement. An INP above 500 milliseconds means that your page has poor responsiveness.
It is important to note that If there are fewer than 50 interactions, INP is measured as the time of the longest interaction. The INP score will be based on the 98th percentile of interactions if there are more than 50.
A screen grab from Web.dev, Google’s web development blog.
Google offers two ways to measure Interaction with Next Paint: “in the field” and “in the lab.” The field refers to Real User Monitoring (RUM) results, which involves measuring all users’ interactions. Once an INP issue is identified using field data, it can be further diagnosed and tested “in the lab” using various tools, including Google’s Lighthouse tool or the Google Chrome Core Web Vitals Google extension. Google offers a good guide on diagnosing these slow interactions in the lab, which is worth checking out for our technical readers.
These “lab” tools help you pinpoint and diagnose the INP issues as you work to correct them. You can isolate and explore the issues before opening tickets to correct them.
Note: For website owners looking to start measuring their core web vitals today, tools like Seosly offer a great list of field and lab tools to aid in this process.
What Causes Poor Interaction to Next Paint?
Google considers three measures when determining INP: Input Delay, Processing Time, and Presentation Delay. A bottleneck in any of these could be problematic.
1. Input Delay: The period from when the user initiates interaction to when the event callbacks begin to run. Possible causes include third-party scripts scheduling many tasks on the main thread, large DOM sizes, and forced reflows due to style changes in JavaScript.
2. Processing Time: This phase consists of the duration for event callbacks to complete their execution. Expensive event callbacks from first-party or third-party JavaScript can delay the browser from presenting the next frame, contributing to high interaction latency.
3. Presentation Delay: This is the time it takes for the browser to render visual updates to reflect the result of an interaction. Causes include large DOM sizes, excessive or unnecessary work in requestAnimationFrame callbacks, and ResizeObserver callbacks with expensive work.
Per Google, Troubleshooting INP is an “iterative process” that involves relying on field data to identify slow interactions, test them in the lab to reproduce the issues, and identify the causes of high interaction latency. By addressing each cause, website owners can improve their Core Web Vitals and enhance user experience.
Conclusion
As Google introduces the “Interaction to Next Paint” as a Core Web Vital, website owners must pay close attention to their site’s responsiveness throughout the user’s interaction. By optimizing Core Web Vitals, site owners can boost their SEO rankings and enhance user experience, reducing bounce rates and improving conversion rates. With INP taking a more comprehensive view of website responsiveness, web developers and site owners must address performance issues and ensure their sites meet users’ expectations. By staying ahead of these changes and leveraging the right tools for measurement, website owners can deliver a smooth and engaging experience to their users, ultimately setting their sites up for success in the ever-evolving digital landscape.